Go Back
Last Updated :
Last Updated :
Jan 15, 2026
Jan 15, 2026

Understand Form 3922: Reporting ESPP Transfers & Stock Basis
As a founder, understanding tax forms related to employee stock purchase plans (ESPP) and stock transactions can be daunting yet critical. One tax document that often puzzles startup leaders is Form 3922, which plays a key role in reporting transfers of stock acquired through an ESPP and in determining your stock basis for tax purposes.
This article is a founder-focused, practical guide to Form 3922, demystifying its purpose, what you need to report, and how it impacts your bookkeeping and tax filing strategies.
What Is Form 3922 and Why It Matters to Founders
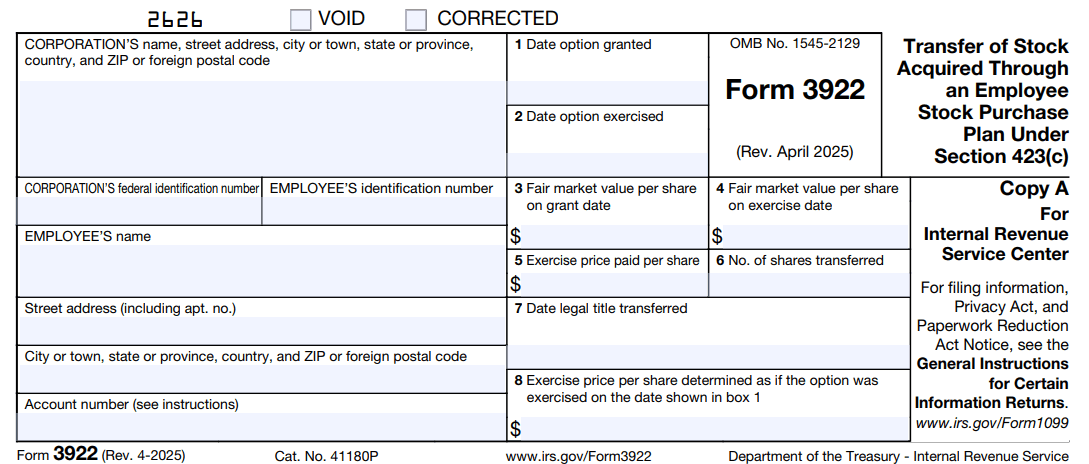
Form 3922, officially titled “Transfer of Stock Acquired Through an Employee Stock Purchase Plan Under Section 423(c),” is used by companies to report the transfer of stock acquired by employees under a qualified ESPP. The form is then provided to employees who purchased stock through the ESPP and to the IRS.
Why founders should care:
Accurate Cost Basis Tracking: For founders and employees, especially in startups offering ESPPs, Form 3922 provides the information needed to establish the stock’s cost basis correctly for capital gains calculations during a sale.
Compliance and Reporting: Companies issuing stock under an ESPP must file Form 3922 with the IRS and provide copies to participating employees, ensuring compliance with IRS rules.
Facilitates Tax Planning: Since ESPP shares often receive favorable tax treatment under Section 423, understanding Form 3922 is foundational for planning stock sales and minimizing unexpected tax liabilities.
For startups in particular, misreporting or neglecting Form 3922 details can lead to confusion around taxable income, missed tax savings, or costly IRS notices.
Jump to related insights on tax reporting and additional forms.
What Information Does Form 3922 Contain?
It's helpful to know what data you and your employees can expect on Form 3922:
Form 3922 Field | Description |
Transfer Date | Date the stock was transferred to the employee |
Employee Information | Name, address, and taxpayer identification |
Employer Information | Company name and EIN |
Stock Details | Class of stock, number of shares transferred |
Fair Market Value (FMV) | FMV of the stock on the transfer date |
Option Exercise Price | Price paid by the employee per share |
Grant Date | Date when the ESPP option was granted |
This information is essential to differentiate between the purchase price and the market value at transfer, which helps calculate the stock basis and identify whether the disposition qualifies for favorable tax treatment.
How Form 3922 Impacts Stock Basis Reporting & Capital Gains Tax
Founders and their finance teams must understand the implications of Form 3922 on stock basis and capital gains to avoid common pitfalls during tax time.
Establishing Cost Basis for ESPP Shares
The cost basis is generally the price the employee paid for the shares (the option exercise price). However, if the FMV on the transfer date is lower, the FMV may be relevant depending on whether there was a qualifying or disqualifying disposition.
Qualified vs. Disqualifying Dispositions
Qualified disposition: Shares held for at least 2 years after grant date and 1 year after purchase date; results in favorable long-term capital gains treatment.
Disqualifying disposition: Shares sold before satisfying these holding periods; compensation income is recognized, typically as ordinary income.
Form 3922 provides the grant date, transfer date, exercise price, and FMV — all vital for founders and employees to categorize the transaction correctly and optimize tax reporting.
Reporting Sales on Tax Returns
When you or your team report ESPP share sales, understanding the correct basis is crucial:
Use grant, purchase, and transfer data from Form 3922 to determine holding periods.
Calculate gains using correct basis (exercise price or FMV, as needed).
Ensure proper classification of the gain (ordinary vs. capital gains) on Form 8949 and Schedule D.
Founders using modern bookkeeping software should confirm this info is synced with their general ledger and year-end reporting tools. To understand broader filing obligations, see our Form 1120-A guide for founders.
Best Practices for Founders Managing ESPP Reporting & Form 3922
Here are founder-smart strategies for seamlessly incorporating Form 3922 into your finance systems:
Coordinate with Payroll, HR, and Admin Teams
Confirm that Form 3922 is filed with the IRS and distributed to employees by the required deadlines.
Double-check accuracy against ESPP plan records and cap table data.
Leverage Automated Bookkeeping Tools
Choose accounting software that supports ESPP tracking and integrates with payroll providers.
Automatically calculate stock basis and match transfers with Form 3922 data.
Educate Your Team
Offer training or FAQs during and after open enrollment or ESPP offering periods.
Help employees understand how to use Form 3922 when preparing their returns.
Monitor ESPP Transactions Throughout the Year
Keep clean records of grant, purchase, and transfer dates.
Review for triggering events or early dispositions with potential tax consequences.
Seek Professional Tax Guidance When Needed
Especially as your company scales, ESPP plans and stock reporting intersect with multistate tax rules, audits, and IPO strategies.
Additional Considerations: Other Tax Forms & Startup-Specific Benefits
How Form 3922 Relates to Other Filings
Form 3921: Reports similar data but for incentive stock options (ISOs).
Form 8949 and Schedule D: Used for reporting capital gains from ESPP share sales.
Form 5329: May apply when certain tax penalties or early distributions are triggered.
Tax Credits and Deductions You Should Know
Startup-friendly incentives include:
R&D Tax Credits
Section 1202 Exclusion
Explore more strategic tax opportunities in our startup tax guide.
Form 3922 Filing Deadlines and IRS Compliance Tips
Here’s a snapshot of what founders need to know:
Employee Copy Deadline: January 31
IRS Filing Deadline:
February 28 (paper)
March 31 (electronic via IRS AIR system)
Filing Method: Electronic filing is encouraged
Accuracy Matters: Incorrect FMV, transfer date, or share count may lead to penalties
For full filing guidance, see the official IRS page on Form 3922.
Empowering Your Startup Through ESPP Clarity
Form 3922 is essential for reporting ESPP stock transfers and establishing accurate cost basis.
Clean processes reduce tax-time stress and help you optimize gains and minimize liabilities.
Tech-enabled bookkeeping plus strategic tax review ensures clean compliance as your company scales.
At Haven, we make ESPP tracking and tax filing stress-free for growing startup teams. We integrate stock-based compensation, tax strategy, and modern finance workflows into a unified solution.
For authoritative IRS details on reporting requirements and official instructions, visit the IRS official website.
As a founder, understanding tax forms related to employee stock purchase plans (ESPP) and stock transactions can be daunting yet critical. One tax document that often puzzles startup leaders is Form 3922, which plays a key role in reporting transfers of stock acquired through an ESPP and in determining your stock basis for tax purposes.
This article is a founder-focused, practical guide to Form 3922, demystifying its purpose, what you need to report, and how it impacts your bookkeeping and tax filing strategies.
What Is Form 3922 and Why It Matters to Founders

Form 3922, officially titled “Transfer of Stock Acquired Through an Employee Stock Purchase Plan Under Section 423(c),” is used by companies to report the transfer of stock acquired by employees under a qualified ESPP. The form is then provided to employees who purchased stock through the ESPP and to the IRS.
Why founders should care:
Accurate Cost Basis Tracking: For founders and employees, especially in startups offering ESPPs, Form 3922 provides the information needed to establish the stock’s cost basis correctly for capital gains calculations during a sale.
Compliance and Reporting: Companies issuing stock under an ESPP must file Form 3922 with the IRS and provide copies to participating employees, ensuring compliance with IRS rules.
Facilitates Tax Planning: Since ESPP shares often receive favorable tax treatment under Section 423, understanding Form 3922 is foundational for planning stock sales and minimizing unexpected tax liabilities.
For startups in particular, misreporting or neglecting Form 3922 details can lead to confusion around taxable income, missed tax savings, or costly IRS notices.
Jump to related insights on tax reporting and additional forms.
What Information Does Form 3922 Contain?
It's helpful to know what data you and your employees can expect on Form 3922:
Form 3922 Field | Description |
Transfer Date | Date the stock was transferred to the employee |
Employee Information | Name, address, and taxpayer identification |
Employer Information | Company name and EIN |
Stock Details | Class of stock, number of shares transferred |
Fair Market Value (FMV) | FMV of the stock on the transfer date |
Option Exercise Price | Price paid by the employee per share |
Grant Date | Date when the ESPP option was granted |
This information is essential to differentiate between the purchase price and the market value at transfer, which helps calculate the stock basis and identify whether the disposition qualifies for favorable tax treatment.
How Form 3922 Impacts Stock Basis Reporting & Capital Gains Tax
Founders and their finance teams must understand the implications of Form 3922 on stock basis and capital gains to avoid common pitfalls during tax time.
Establishing Cost Basis for ESPP Shares
The cost basis is generally the price the employee paid for the shares (the option exercise price). However, if the FMV on the transfer date is lower, the FMV may be relevant depending on whether there was a qualifying or disqualifying disposition.
Qualified vs. Disqualifying Dispositions
Qualified disposition: Shares held for at least 2 years after grant date and 1 year after purchase date; results in favorable long-term capital gains treatment.
Disqualifying disposition: Shares sold before satisfying these holding periods; compensation income is recognized, typically as ordinary income.
Form 3922 provides the grant date, transfer date, exercise price, and FMV — all vital for founders and employees to categorize the transaction correctly and optimize tax reporting.
Reporting Sales on Tax Returns
When you or your team report ESPP share sales, understanding the correct basis is crucial:
Use grant, purchase, and transfer data from Form 3922 to determine holding periods.
Calculate gains using correct basis (exercise price or FMV, as needed).
Ensure proper classification of the gain (ordinary vs. capital gains) on Form 8949 and Schedule D.
Founders using modern bookkeeping software should confirm this info is synced with their general ledger and year-end reporting tools. To understand broader filing obligations, see our Form 1120-A guide for founders.
Best Practices for Founders Managing ESPP Reporting & Form 3922
Here are founder-smart strategies for seamlessly incorporating Form 3922 into your finance systems:
Coordinate with Payroll, HR, and Admin Teams
Confirm that Form 3922 is filed with the IRS and distributed to employees by the required deadlines.
Double-check accuracy against ESPP plan records and cap table data.

Leverage Automated Bookkeeping Tools
Choose accounting software that supports ESPP tracking and integrates with payroll providers.
Automatically calculate stock basis and match transfers with Form 3922 data.
Educate Your Team
Offer training or FAQs during and after open enrollment or ESPP offering periods.
Help employees understand how to use Form 3922 when preparing their returns.
Monitor ESPP Transactions Throughout the Year
Keep clean records of grant, purchase, and transfer dates.
Review for triggering events or early dispositions with potential tax consequences.
Seek Professional Tax Guidance When Needed
Especially as your company scales, ESPP plans and stock reporting intersect with multistate tax rules, audits, and IPO strategies.
Additional Considerations: Other Tax Forms & Startup-Specific Benefits
How Form 3922 Relates to Other Filings
Form 3921: Reports similar data but for incentive stock options (ISOs).
Form 8949 and Schedule D: Used for reporting capital gains from ESPP share sales.
Form 5329: May apply when certain tax penalties or early distributions are triggered.
Tax Credits and Deductions You Should Know
Startup-friendly incentives include:
R&D Tax Credits
Section 1202 Exclusion
Explore more strategic tax opportunities in our startup tax guide.
Form 3922 Filing Deadlines and IRS Compliance Tips
Here’s a snapshot of what founders need to know:
Employee Copy Deadline: January 31
IRS Filing Deadline:
February 28 (paper)
March 31 (electronic via IRS AIR system)
Filing Method: Electronic filing is encouraged
Accuracy Matters: Incorrect FMV, transfer date, or share count may lead to penalties
For full filing guidance, see the official IRS page on Form 3922.

Empowering Your Startup Through ESPP Clarity
Form 3922 is essential for reporting ESPP stock transfers and establishing accurate cost basis.
Clean processes reduce tax-time stress and help you optimize gains and minimize liabilities.
Tech-enabled bookkeeping plus strategic tax review ensures clean compliance as your company scales.
At Haven, we make ESPP tracking and tax filing stress-free for growing startup teams. We integrate stock-based compensation, tax strategy, and modern finance workflows into a unified solution.
For authoritative IRS details on reporting requirements and official instructions, visit the IRS official website.
This article was co-written by:
Content
This article was co-written by:
2026
© Haven All Rights Reserved
2026
© Haven All Rights Reserved
2026