Go Back
Last Updated :
Last Updated :
Jan 5, 2026
Jan 5, 2026

Form 1042 Filing Guide: Withholding Tax for Foreign Persons
For founders of U.S. startups, agencies, and e-commerce companies with international stakeholders or vendors, Form 1042 is a critical part of your tax compliance toolkit. Understanding this form minimizes financial risk and ensures your global operations remain IRS-compliant.
What Is Form 1042?
Form 1042 is the Annual Withholding Tax Return for U.S. Source Income of Foreign Persons. It is used by the U.S. "withholding agents" to report tax withheld on payments made to foreign recipients.
Key Definitions for Founders
Withholding Agent: Any U.S. company or person who makes a payment to a foreign person that may be subject to withholding tax.
Foreign Person: Nonresident aliens, foreign partnerships, foreign corporations, or foreign estates/trusts.
U.S. Source Income: Income originating from within the U.S., such as dividends from a U.S. corporation or royalties for software used in the U.S..
Who Needs to File?
You must file Form 1042 if your company makes payments of U.S.-source income to foreign persons. Common scenarios for startups include:
Royalties: Paying a foreign entity for software licenses or digital content.
Dividends: Distributing profits to foreign investors or shareholders.
Services: Paying a foreign contractor for work physically performed in the U.S..
Interest: Making interest payments on debt held by foreign investors.
How Withholding Tax Works
Withholding tax is a mechanism where your company (the payer) deducts a percentage of a payment and sends it directly to the IRS. This ensures the U.S. collects tax on income before it leaves the country.
Common Withholding Rates
The statutory default rate is 30%, but this is often reduced by international tax treaties.
Payment Type | Default Rate | Common Treaty Reductions |
Dividends | 30% | Often 15% or 0% |
Interest | 30% | Often 0% |
Royalties | 30% | Varies widely by country |
Step-by-Step: How to Fill Out Form 1042
Step 1: Record Federal Tax Liability (Section 1)
This section is a detailed record of your tax liability for the year, broken down by month and specific periods (the 7th, 15th, 22nd, and last day of each month).
Note: You must report the liability based on when the payment was made, not when the deposit was sent.
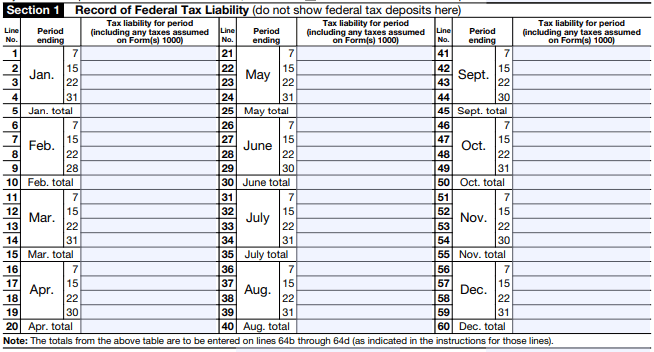
Step 2: Reconcile with Form 1042-S (Section 2)
In this section, you summarize the total gross amounts paid and taxes withheld.
Line 61: Enter the number of individual Forms 1042-S you filed (the specific forms given to each recipient).
Line 62: Total the gross amounts of U.S.-source income reported across all forms.
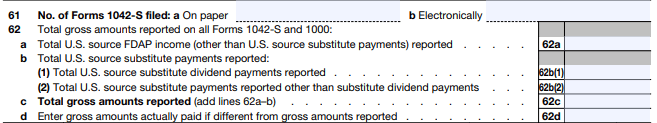
Step 3: Calculate Total Tax and Payments
Line 64: Calculate the total tax liability for the year.
Line 65: Enter the total amount of federal tax deposits you made throughout the year.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Missing W-8 Forms: Failing to collect a valid Form W-8 (like W-8BEN or W-8BEN-E) from your foreign vendors before paying them.
Incorrect Rates: Applying the 30% default rate when a lower treaty rate was available—or vice versa.
Late Deposits: The IRS requires deposits to be made frequently (sometimes within days of a payment); missing these deadlines triggers automatic penalties.
When is Form 1042 Due?
Form 1042 is due annually by March 15th of the year following the payments. You must also provide the corresponding Form 1042-S to your foreign recipients by this same date.
Simplify International Compliance with Haven
Managing international withholding is complex and carries high penalty risks. Haven’s founder-friendly tax services take the guesswork out of Form 1042.
Automated Withholding: We help you track and deposit taxes in real-time.
W-8 Management: We ensure you have the correct documentation for every foreign stakeholder.
Agile Filing: Our platform generates accurate Forms 1042 and 1042-S, so you can focus on scaling your vision.
For founders of U.S. startups, agencies, and e-commerce companies with international stakeholders or vendors, Form 1042 is a critical part of your tax compliance toolkit. Understanding this form minimizes financial risk and ensures your global operations remain IRS-compliant.
What Is Form 1042?
Form 1042 is the Annual Withholding Tax Return for U.S. Source Income of Foreign Persons. It is used by the U.S. "withholding agents" to report tax withheld on payments made to foreign recipients.
Key Definitions for Founders
Withholding Agent: Any U.S. company or person who makes a payment to a foreign person that may be subject to withholding tax.
Foreign Person: Nonresident aliens, foreign partnerships, foreign corporations, or foreign estates/trusts.
U.S. Source Income: Income originating from within the U.S., such as dividends from a U.S. corporation or royalties for software used in the U.S..
Who Needs to File?
You must file Form 1042 if your company makes payments of U.S.-source income to foreign persons. Common scenarios for startups include:
Royalties: Paying a foreign entity for software licenses or digital content.
Dividends: Distributing profits to foreign investors or shareholders.
Services: Paying a foreign contractor for work physically performed in the U.S..
Interest: Making interest payments on debt held by foreign investors.
How Withholding Tax Works
Withholding tax is a mechanism where your company (the payer) deducts a percentage of a payment and sends it directly to the IRS. This ensures the U.S. collects tax on income before it leaves the country.
Common Withholding Rates
The statutory default rate is 30%, but this is often reduced by international tax treaties.
Payment Type | Default Rate | Common Treaty Reductions |
Dividends | 30% | Often 15% or 0% |
Interest | 30% | Often 0% |
Royalties | 30% | Varies widely by country |
Step-by-Step: How to Fill Out Form 1042
Step 1: Record Federal Tax Liability (Section 1)
This section is a detailed record of your tax liability for the year, broken down by month and specific periods (the 7th, 15th, 22nd, and last day of each month).
Note: You must report the liability based on when the payment was made, not when the deposit was sent.

Step 2: Reconcile with Form 1042-S (Section 2)
In this section, you summarize the total gross amounts paid and taxes withheld.
Line 61: Enter the number of individual Forms 1042-S you filed (the specific forms given to each recipient).
Line 62: Total the gross amounts of U.S.-source income reported across all forms.

Step 3: Calculate Total Tax and Payments
Line 64: Calculate the total tax liability for the year.
Line 65: Enter the total amount of federal tax deposits you made throughout the year.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Missing W-8 Forms: Failing to collect a valid Form W-8 (like W-8BEN or W-8BEN-E) from your foreign vendors before paying them.
Incorrect Rates: Applying the 30% default rate when a lower treaty rate was available—or vice versa.
Late Deposits: The IRS requires deposits to be made frequently (sometimes within days of a payment); missing these deadlines triggers automatic penalties.
When is Form 1042 Due?
Form 1042 is due annually by March 15th of the year following the payments. You must also provide the corresponding Form 1042-S to your foreign recipients by this same date.
Simplify International Compliance with Haven
Managing international withholding is complex and carries high penalty risks. Haven’s founder-friendly tax services take the guesswork out of Form 1042.
Automated Withholding: We help you track and deposit taxes in real-time.
W-8 Management: We ensure you have the correct documentation for every foreign stakeholder.
Agile Filing: Our platform generates accurate Forms 1042 and 1042-S, so you can focus on scaling your vision.
This article was co-written by:
Content
This article was co-written by:
2026
© Haven All Rights Reserved
2026
© Haven All Rights Reserved
2026