Go Back
Last Updated :
Last Updated :
Feb 6, 2026
Feb 6, 2026



Preparing for a Financial Audit: A Checklist for Series A Founders
As a Series A founder, the stretch from seed stage to scaling brings a deeper dive into financial scrutiny. Whether you’re securing additional capital, satisfying investor demands, or simply ensuring robust financial governance, financial audit prep becomes a pivotal step.
Unlike earlier informal reviews, these audits require comprehensive documentation and adherence to standards like GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles) and GAAS (Generally Accepted Auditing Standards).
This article serves as a practical, founder-friendly guide to prepare efficiently and confidently for a financial audit ahead of your next funding milestone or strategic review.
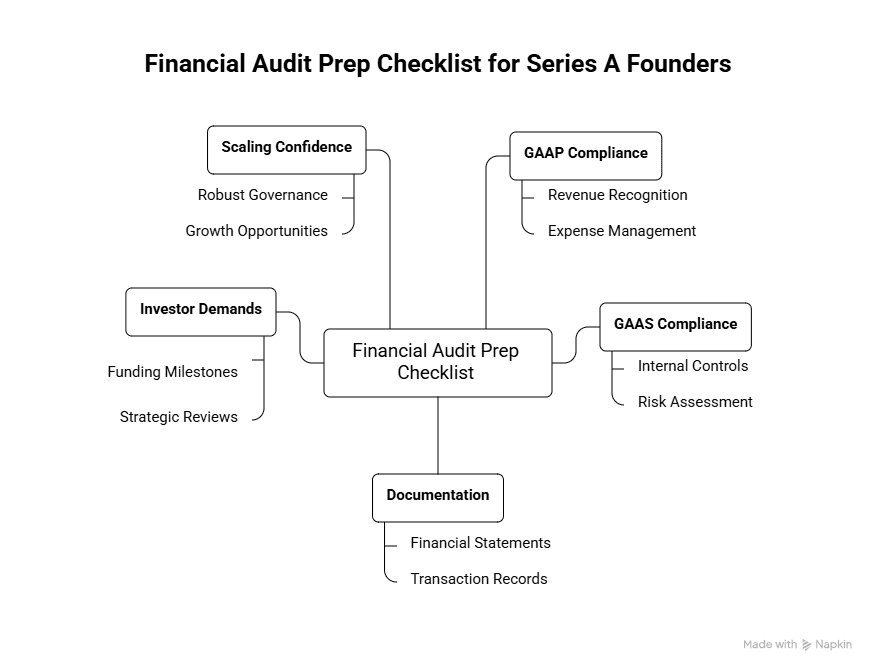
Why Financial Audit Prep Matters for Series A Startups
At Series A, startups typically face more formal and detailed financial examinations compared to seed rounds. This transition is driven by:
Growing investor expectations for transparency and accuracy.
Increased complexity in revenue recognition, expenses, and equity structures.
Regulatory compliance when scaling from private to potential public markets.
Preparing well avoids last-minute scrambling, costly audit findings, and potential delays in financing or business decisions.
Key Elements of Financial Audit Prep Every Founder Should Know
Before diving into a step-by-step checklist, understanding a few key concepts and documents involved in audits helps align expectations.
Element | Description | Why It Matters |
Financial Statements | Balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement prepared according to GAAP | Foundation for auditors to verify accuracy |
Supporting Documentation | Bank statements, contracts, invoices, payroll records, and funding documents | Provides evidence backing financial numbers |
Internal Controls | Policies and procedures ensuring accuracy and preventing fraud | Auditors assess control effectiveness |
Trial Balance and General Ledger | Aggregate and detailed transaction records organized for financial reporting | Essential for auditors testing balances |
Compliance Requirements | Industry-specific or regulatory rules, SOX compliance if public or scaling thereto | Failure to comply can materially impact results |
Understanding these core elements frames the rest of your preparation focus effectively.
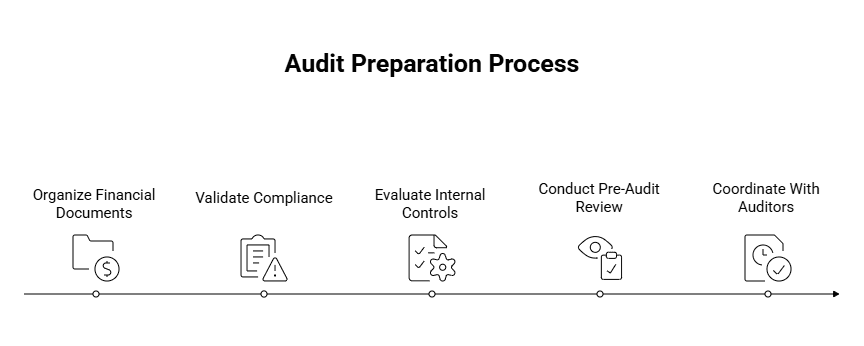
Financial Audit Prep Checklist for Series A Founders
1. Organize Your Financial Documents Early
Prepare a centralized digital folder or cloud repository containing:
Complete financial statements for the audit period, ideally reviewed internally or by your accounting team.
General ledger and trial balances match the financial statements.
Supporting documents including:
Bank reconciliations and bank statements.
Invoices (sales and purchase).
Payroll records with tax filings.
Capitalization table and equity documents post any financing rounds.
Contracts or agreements with customers, vendors, or partners.
Loan agreements and notes payable details.
Pro Tip: Keeping digital and well-categorized records will accelerate auditor workflows and reduce clarification cycles.
2. Validate Compliance with Accounting Standards
Your financials should adhere strictly to GAAP. Engage your internal finance lead or external accounting service to:
Verify revenue recognition policies align with ASC 606 guidelines.
Confirm expense categorization is consistent and justifiable.
Ensure capitalization and amortization follow accepted methods.
Companies leveraging modern bookkeeping and reporting services often benefit here by reducing manual errors.
3. Evaluate and Strengthen Internal Controls
Auditors pay significant attention to your internal control environment because it mitigates risks such as fraud or material misstatements.
Document your existing financial policies.
Identify key control points like approvals, reconciliations, and segregation of duties.
Address any known weaknesses proactively—e.g., enhance expense approval chains or implement regular reconciliation schedules.
This step reduces audit findings and enhances your startup’s financial credibility.
4. Conduct a Pre-Audit Review
Ideally several weeks before the scheduled audit:
Run a detailed self-audit with your finance team to cross-check financial statements against source documentation.
Reconcile account balances and investigate discrepancies.
Prepare explanations or additional evidence for unusual transactions or adjustments.
Effective pre-audit reviews highlight gaps early, allowing founders to fix issues without external pressure.
5. Coordinate With Your Auditors Efficiently
Proactively managing auditor interactions saves crucial time:
Share your prepared documents promptly and in an organized manner.
Assign a point of contact within your team for quick responses.
Provide contextual explanations on critical accounts, e.g., explaining R&D tax credit claims or unusual revenue spikes.
Utilize technology platforms for secure data sharing and progress tracking.
Transparency and responsiveness demonstrate your startup’s commitment to accuracy, reassuring auditors and stakeholders alike.
Common Audit Areas to Focus on for Startups
Understanding what areas auditors prioritize can help founders allocate effort judiciously.
Audit Area | Focus Points |
Revenue Recognition | Are sales recorded in the correct periods? Are deferred revenues and refunds handled properly? |
R&D Expense and Credits | Documentation of research costs; impact on tax credits; justification of capitalization. |
Equity and Funding Transactions | Accurate tracking of stock issuances, warrants, and convertible notes. |
Cash and Bank Balances | Reconciliations with bank statements to confirm liquidity and fraud control. |
Payroll and Tax Withholding | Compliance with employment tax regulations and accurate accruals for bonuses, benefits. |
Especially for startups engaged in technology development, a careful review of R&D tax credit claims and associated documentation is critical. This not only impacts audits but also your tax position and funding attractiveness.
Post-Audit: Utilizing Insights to Strengthen Your Financial Operations
Once the audit is concluded, take these steps to convert findings into growth:
Review the auditor’s report and management letter closely.
Prioritize implementing recommendations related to internal controls and compliance gaps.
Update your accounting and bookkeeping processes as needed.
Consider ongoing reporting to maintain continuous readiness.
Incorporating these improvements accelerates your startup’s maturity curve and builds confidence with stakeholders, preparing for future rounds or public offerings.
Example: How a Startup Successfully Prepped for Its Financial Audit
Consider a SaaS startup closing Series A funding. The founders anticipated an auditor review emphasizing revenue recognition and R&D credits. By engaging a specialized bookkeeping and reporting partner early, they:
Implemented automated revenue tracking consistent with ASC standards.
Maintained digital logs of all R&D activities and expenditures supporting tax credit claims.
Performed monthly reconciliations and quarterly trial balance reviews to avoid surprises.
Established clear internal controls documented in operations manuals.
This preparation reduced auditor queries by 40%, shortened audit duration by 30%, and helped secure a smooth financing round without budget overruns on audit costs.
Leveraging Expert Services for Modern, Startup-Ready Financial Audit Prep
While founder-led oversight is critical, startups can’t do it all alone. Using contemporary bookkeeping, tax filing, and R&D consulting firms specializing in early-growth startups can be a game changer. They bring:
Expertise aligned with startup financial realities.
Technology leveraged for accuracy and efficiency.
Proactive audit preparedness protocols designed around funding cycles and investor expectations.
Making Financial Audit Prep Work for Your Startup
For Series A founders, financial audit prep is not just a compliance checkbox – it is a strategic lever to showcase your startup’s financial discipline and operational maturity. Early and thorough preparation, grounded in robust bookkeeping and aligned with GAAP/GAAS principles, enables smoother audits and more confident investor discussions.
Taking a founder-friendly, pragmatic approach backed by expert partners can make this demanding process a business advantage, not a burden. Begin months ahead, focus on documentation and controls, and turn the audit into a milestone of your startup’s growth journey.
By integrating these practices, you not only survive your financial audit—you strengthen your startup’s foundation for rapid, scalable success.
As a Series A founder, the stretch from seed stage to scaling brings a deeper dive into financial scrutiny. Whether you’re securing additional capital, satisfying investor demands, or simply ensuring robust financial governance, financial audit prep becomes a pivotal step.
Unlike earlier informal reviews, these audits require comprehensive documentation and adherence to standards like GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles) and GAAS (Generally Accepted Auditing Standards).
This article serves as a practical, founder-friendly guide to prepare efficiently and confidently for a financial audit ahead of your next funding milestone or strategic review.

Why Financial Audit Prep Matters for Series A Startups
At Series A, startups typically face more formal and detailed financial examinations compared to seed rounds. This transition is driven by:
Growing investor expectations for transparency and accuracy.
Increased complexity in revenue recognition, expenses, and equity structures.
Regulatory compliance when scaling from private to potential public markets.
Preparing well avoids last-minute scrambling, costly audit findings, and potential delays in financing or business decisions.
Key Elements of Financial Audit Prep Every Founder Should Know
Before diving into a step-by-step checklist, understanding a few key concepts and documents involved in audits helps align expectations.
Element | Description | Why It Matters |
Financial Statements | Balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement prepared according to GAAP | Foundation for auditors to verify accuracy |
Supporting Documentation | Bank statements, contracts, invoices, payroll records, and funding documents | Provides evidence backing financial numbers |
Internal Controls | Policies and procedures ensuring accuracy and preventing fraud | Auditors assess control effectiveness |
Trial Balance and General Ledger | Aggregate and detailed transaction records organized for financial reporting | Essential for auditors testing balances |
Compliance Requirements | Industry-specific or regulatory rules, SOX compliance if public or scaling thereto | Failure to comply can materially impact results |
Understanding these core elements frames the rest of your preparation focus effectively.
Financial Audit Prep Checklist for Series A Founders
1. Organize Your Financial Documents Early
Prepare a centralized digital folder or cloud repository containing:
Complete financial statements for the audit period, ideally reviewed internally or by your accounting team.
General ledger and trial balances match the financial statements.
Supporting documents including:
Bank reconciliations and bank statements.
Invoices (sales and purchase).
Payroll records with tax filings.
Capitalization table and equity documents post any financing rounds.
Contracts or agreements with customers, vendors, or partners.
Loan agreements and notes payable details.
Pro Tip: Keeping digital and well-categorized records will accelerate auditor workflows and reduce clarification cycles.
2. Validate Compliance with Accounting Standards
Your financials should adhere strictly to GAAP. Engage your internal finance lead or external accounting service to:
Verify revenue recognition policies align with ASC 606 guidelines.
Confirm expense categorization is consistent and justifiable.
Ensure capitalization and amortization follow accepted methods.
Companies leveraging modern bookkeeping and reporting services often benefit here by reducing manual errors.
3. Evaluate and Strengthen Internal Controls
Auditors pay significant attention to your internal control environment because it mitigates risks such as fraud or material misstatements.
Document your existing financial policies.
Identify key control points like approvals, reconciliations, and segregation of duties.
Address any known weaknesses proactively—e.g., enhance expense approval chains or implement regular reconciliation schedules.
This step reduces audit findings and enhances your startup’s financial credibility.
4. Conduct a Pre-Audit Review
Ideally several weeks before the scheduled audit:
Run a detailed self-audit with your finance team to cross-check financial statements against source documentation.
Reconcile account balances and investigate discrepancies.
Prepare explanations or additional evidence for unusual transactions or adjustments.
Effective pre-audit reviews highlight gaps early, allowing founders to fix issues without external pressure.
5. Coordinate With Your Auditors Efficiently
Proactively managing auditor interactions saves crucial time:
Share your prepared documents promptly and in an organized manner.
Assign a point of contact within your team for quick responses.
Provide contextual explanations on critical accounts, e.g., explaining R&D tax credit claims or unusual revenue spikes.
Utilize technology platforms for secure data sharing and progress tracking.
Transparency and responsiveness demonstrate your startup’s commitment to accuracy, reassuring auditors and stakeholders alike.

Common Audit Areas to Focus on for Startups
Understanding what areas auditors prioritize can help founders allocate effort judiciously.
Audit Area | Focus Points |
Revenue Recognition | Are sales recorded in the correct periods? Are deferred revenues and refunds handled properly? |
R&D Expense and Credits | Documentation of research costs; impact on tax credits; justification of capitalization. |
Equity and Funding Transactions | Accurate tracking of stock issuances, warrants, and convertible notes. |
Cash and Bank Balances | Reconciliations with bank statements to confirm liquidity and fraud control. |
Payroll and Tax Withholding | Compliance with employment tax regulations and accurate accruals for bonuses, benefits. |
Especially for startups engaged in technology development, a careful review of R&D tax credit claims and associated documentation is critical. This not only impacts audits but also your tax position and funding attractiveness.
Post-Audit: Utilizing Insights to Strengthen Your Financial Operations
Once the audit is concluded, take these steps to convert findings into growth:
Review the auditor’s report and management letter closely.
Prioritize implementing recommendations related to internal controls and compliance gaps.
Update your accounting and bookkeeping processes as needed.
Consider ongoing reporting to maintain continuous readiness.
Incorporating these improvements accelerates your startup’s maturity curve and builds confidence with stakeholders, preparing for future rounds or public offerings.
Example: How a Startup Successfully Prepped for Its Financial Audit
Consider a SaaS startup closing Series A funding. The founders anticipated an auditor review emphasizing revenue recognition and R&D credits. By engaging a specialized bookkeeping and reporting partner early, they:
Implemented automated revenue tracking consistent with ASC standards.
Maintained digital logs of all R&D activities and expenditures supporting tax credit claims.
Performed monthly reconciliations and quarterly trial balance reviews to avoid surprises.
Established clear internal controls documented in operations manuals.
This preparation reduced auditor queries by 40%, shortened audit duration by 30%, and helped secure a smooth financing round without budget overruns on audit costs.
Leveraging Expert Services for Modern, Startup-Ready Financial Audit Prep
While founder-led oversight is critical, startups can’t do it all alone. Using contemporary bookkeeping, tax filing, and R&D consulting firms specializing in early-growth startups can be a game changer. They bring:
Expertise aligned with startup financial realities.
Technology leveraged for accuracy and efficiency.
Proactive audit preparedness protocols designed around funding cycles and investor expectations.
Making Financial Audit Prep Work for Your Startup
For Series A founders, financial audit prep is not just a compliance checkbox – it is a strategic lever to showcase your startup’s financial discipline and operational maturity. Early and thorough preparation, grounded in robust bookkeeping and aligned with GAAP/GAAS principles, enables smoother audits and more confident investor discussions.
Taking a founder-friendly, pragmatic approach backed by expert partners can make this demanding process a business advantage, not a burden. Begin months ahead, focus on documentation and controls, and turn the audit into a milestone of your startup’s growth journey.
By integrating these practices, you not only survive your financial audit—you strengthen your startup’s foundation for rapid, scalable success.
This article was co-written by:
Content
This article was co-written by:
2026
© Haven All Rights Reserved
2026
© Haven All Rights Reserved
2026